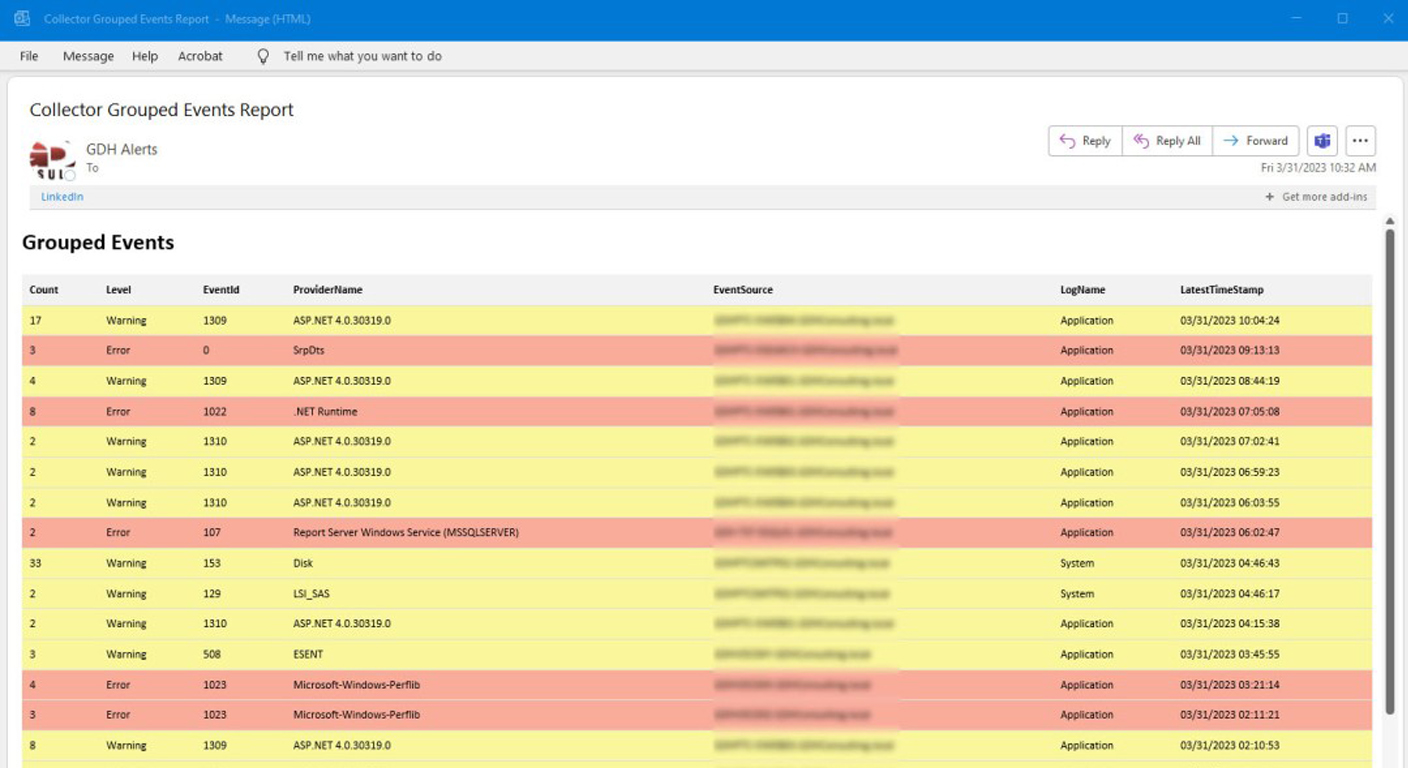
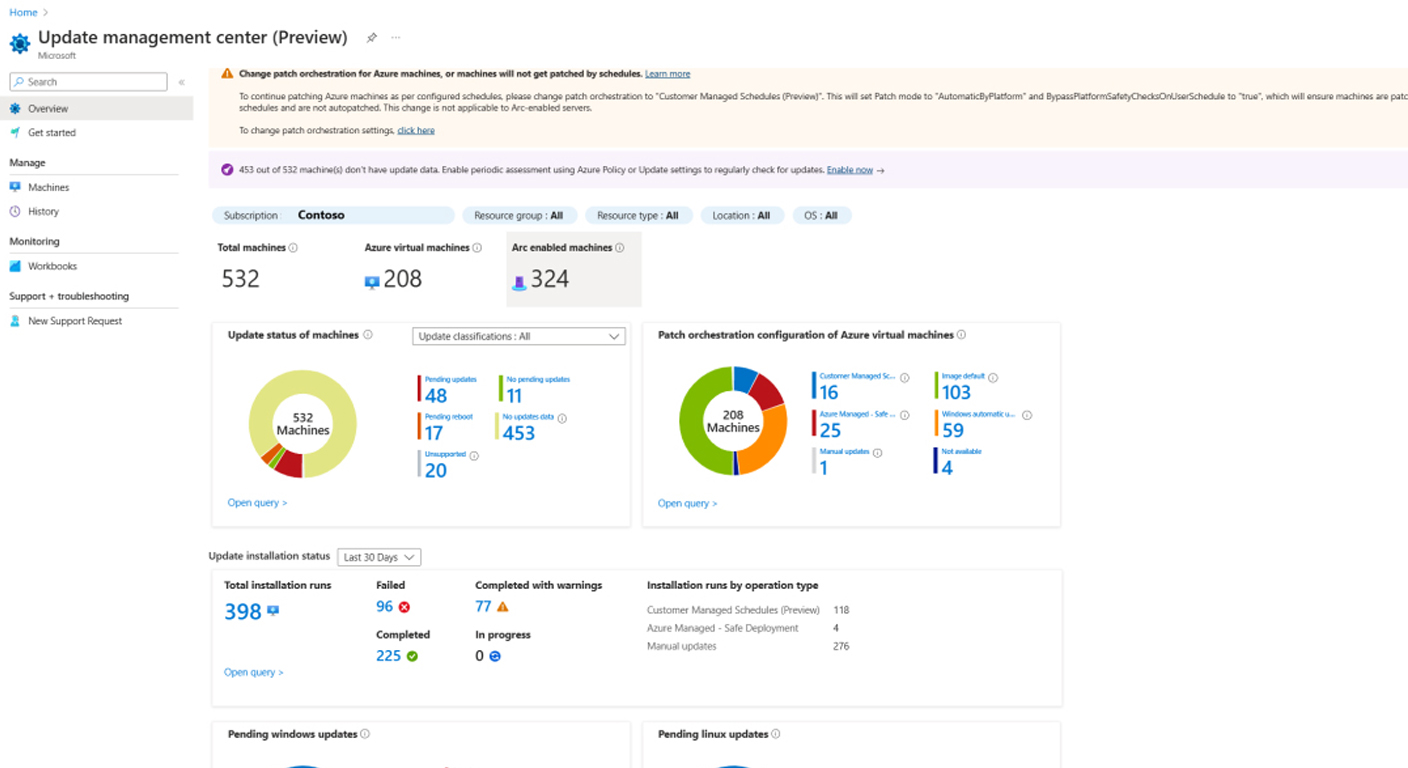
Endpoint security is crucial for protecting devices like computers, smartphones, and tablets that connect to your corporate network. These endpoints can be entry points for cyber threats, making their protection vital.
Key Components of Endpoint Security:
Antivirus and Antimalware: These tools detect and remove malicious software, safeguarding your devices from various threats.
Firewalls: They monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic, acting as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): IDPS continuously monitor network traffic to identify and block suspicious activities, preventing potential breaches.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions prevent unauthorized data transfers, ensuring sensitive information remains secure.
Patch Management: Regular updates and patches fix vulnerabilities in software and operating systems, reducing the risk of exploitation.
Machine Learning and AI: Advanced technologies analyze patterns to detect and respond to emerging threats more effectively.
Common Attack Vectors:
Phishing Emails: Deceptive emails trick users into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware.
Malvertising: Compromised advertisements distribute malware to unsuspecting users.
Removable Media: Infected USB drives can introduce malware into your network.
Weak Passwords: Easily guessable or reused passwords make unauthorized access easier for attackers.
Unsecured IoT Devices: Internet of Things devices with poor security can serve as entry points for cybercriminals.
Best Practices for Endpoint Security:
Implement a Zero Trust Model: Assume that threats could be both external and internal, and verify all access requests.
Enforce Strong Password Policies: Require complex, unique passwords and regular updates.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security beyond just passwords.
Regular Employee Training: Educate staff about recognizing phishing attempts and other cyber threats.
Continuous Monitoring: Keep an eye on network activities to detect and respond to anomalies promptly.
By focusing on these aspects, you can strengthen your organization’s defenses against cyber threats and protect your network’s endpoints effectively.